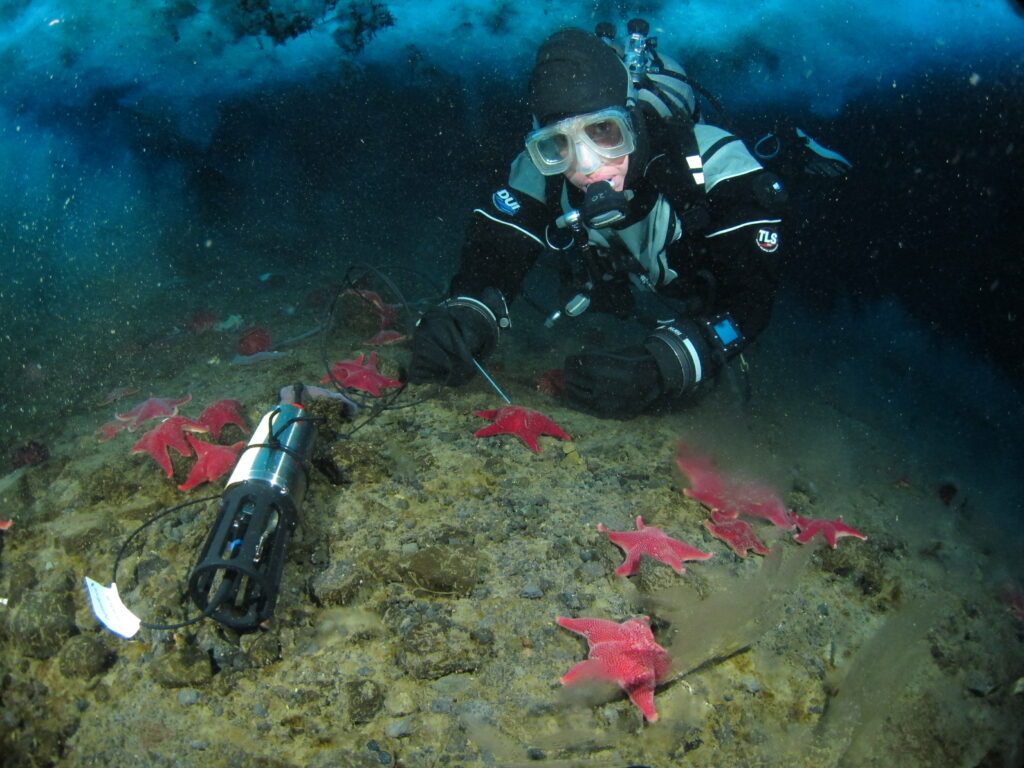

Introduction
Sea star wasting syndrome (SSWS) has emerged as a devastating phenomenon affecting starfish populations worldwide and fundamentally altering coastal marine ecosystems. In search of better understanding of its causes, the researchers from Oregon State University and the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa embarked on a groundbreaking study in 2023 to explore the first-known SSWS outbreaks in the high Antarctic near McMurdo Station. With the leading hypothesis of hypoxia at the starfish dermis and water interface being an important driver, they focused on studying the oxygen dynamics at the benthos and the surfaces of starfish at two sites where outbreaks of SSWS were documented in 2019 and 2022.
Method
Using a diver-deployed AquapHOx-LX deep sea logger with OXROB10-SUB robust oxygen probe, the research team measured oxygen levels at the benthos (sea floor) and on the surfaces of both healthy and diseased starfish. The study sites were carefully chosen to compare oxygen levels within SSWS-affected areas against those where starfish remained unaffected.
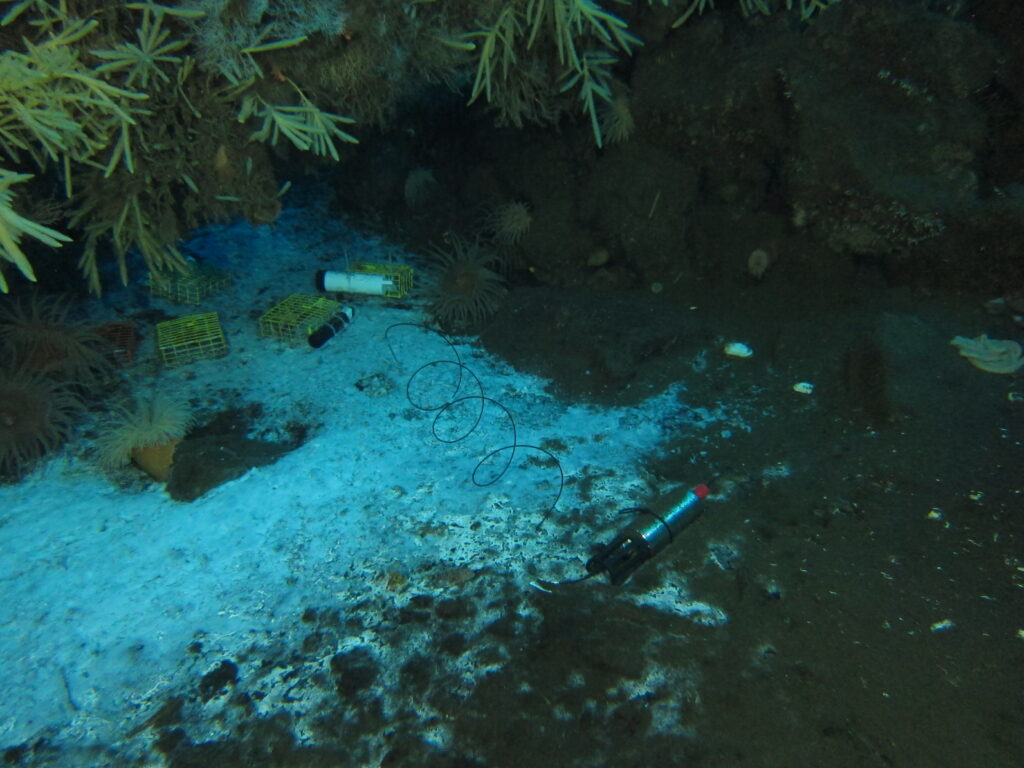

Preliminary Findings
The researchers made the following observations:
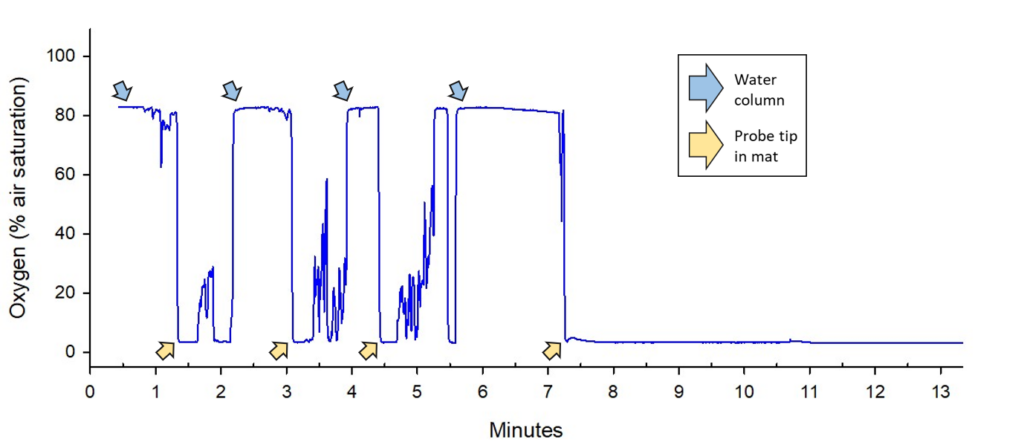
- Beggiatoa Mats, Methane Seep and Oxygen Depletion: A large outbreak of SSWS was co-located with a methane seep with large associated mats of sulfur-oxidizing Beggiatoa. Oxygen levels were notably low adjacent to the Beggiatoa mats, with anoxic conditions detected within millimeters of the mat surface. This indicates significant microbial oxygen consuming activity in localized areas such as these.
- Surface Oxygen of Starfish: No significant differences in surface oxygen levels were detected between healthy and diseased starfish likely because the fish had no visible bacterial overgrowth and the metabolic oxygen drawdown is quite low.
Conclusion
These results suggest that organic inputs, such as ocean warming or methane escapes, stimulate microbial growth on the benthos and in water columns and cause reduction in oxygen concentrations creating hypoxic conditions. Given that hypoxia is a suspected proximal trigger of SSWS, such events may lead to its more frequent outbreaks in the Southern Ocean.
Implications and Future Research
Understanding the intricate relationship between microbial activity, oxygen dynamics, and SSWS is crucial for predicting and mitigating future outbreaks. Further research could focus on:
- Long-term Monitoring: Continuously monitoring oxygen dynamics at SSWS outbreak sites to capture seasonal variations and long-term trends.
- Microbial Interactions: Investigating how different microbial communities interact with starfish and contribute to disease outbreaks.
- Climate Change Impacts: Assessing how climate-driven changes in ocean conditions, such as warming and altered methane cycles, influence microbial activity and subsequent SSWS outbreaks.
Click this link to read a more detailed summary of the study results by Oregon State University and University of Hawai’i at Mānoa.
If you are looking for an underwater sensor system solution for your marine research, contact us today and we will be happy to help you select the best configuration for your project.
